Przemyslaw Lisinski, Wlodzimierz Samborski
Faculty and Clinic of Rheumatology and Rehabilitation
Medical University in Poznan
Background
The investigated preparation was a dietary supplement specially designed for people with joint problems. Its formula provides carefully selected plants, which active constituents have been extracted in special technology ensuring better bioavailability and hence efficacy. Each capsule provides 6 plant extracts that possibly have positive action on synoviocytes1 (cells that form inner layer of synovial membrane and chondrocytes2 (cells forming joint cartilage).
The purpose of this study was an evaluation of the efficacy and tolerance of the preparation providing plant extracts in patients with osteoarthritis (OA).
Subjects and Methods
There were 60 subjects qualified for the study with osteoarthritis stage II/III acc. to Kellgren-Lawrence Radiological Assessment3. The investigation was conducted as double blind study4. Subjects were divided into two randomised5 parallel groups. After one week of wash-out period6, one group received active (investigated) preparation (verum group) and the other group received placebo7 (placebo group) for 6 weeks. Investigated patients received an average daily dosage of one capsule twice a day. Patients with very big body mass (BMI ≥ 30) took doubled daily dose.
Patients were evaluated before starting the study, and after 3 and 6 weeks. Following parameters were evaluated:
 general condition by the help of Likert scale8
general condition by the help of Likert scale8 quality of life by questionnaire SF-129
quality of life by questionnaire SF-129 intensity of pain in last 24 hours
intensity of pain in last 24 hours intensity of pain after 15 meters walk
intensity of pain after 15 meters walk integrated WOMAC Index 10
integrated WOMAC Index 10
Intensity of pain was evaluated with use of the visual-analogue scale – so called VAS11.
Patients that had interrupted the study were evaluated till the moment they stopped the study.
All side and/or undesired effects were registered. Furthermore, each time were taken blood samples for testing the basic biochemical parameters and liver and kidney function.
In the statistical analysis of the study, a nonparametric rank sum test was used, the so-called Mann-Whitney U test, also known as the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon (MWW) test. The standard error of the mean (SEM) was applied. The standard deviation (SD) does not take into account the sample size. The standard error of the mean makes it possible to determine the confidence intervals for the mean, i.e. to determine with a certain probability from which values to which values the average of a given feature in a given population falls. Due to the small size of the group, for the reliability of the statistical analysis, we used not the standard error of the mean, but its doubled value (2SEM).
Results
Pain Assessment
Pain at Rest
The pain that patient has experienced at rest was evaluated 24 hours before the study and after 3 and 6 weeks of product consumption. The placebo group showed a reduction in pain intensity by an average of 7 mm after 3 weeks and 8 mm after 6 weeks[8]. In the group receiving the active preparation a decrease in the intensity of pain was observed by 18 and 30 mm after 3 and 6 weeks, respectively.
These differences were highly statistically significant in favor of the active formulation; confidence interval p ≤ 0.05 after 3 weeks and p ≤ 0.002 after 6 weeks. It is assumed that the reduction of pain intensity by the value of 15 mm according to VAS is of significant clinical importance. After 6 weeks of taking the test preparation, the reduction of pain intensity by 30 mm and more (i.e. twice more than the assumed clinically significant value) was found in 79% of the respondents.
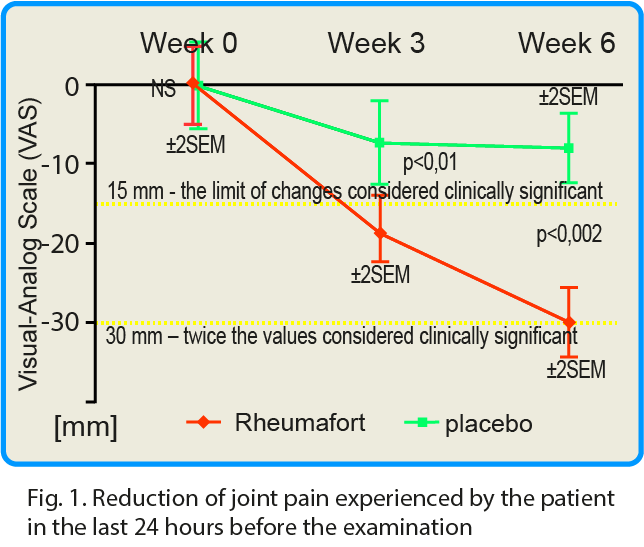
click the graph in order to magnificate.
Pain When Walking
Changes in pain intensity after a 15-yards walk were also assessed. In the group receiving the investigated preparation, a clinically significant reduction in pain intensity after walking was found compared to the placebo group. The mean value of pain intensity for the whole group receiving the preparation containing plant extracts decreased by 40 mm according to the VAS scale after 6 weeks. In the control group (placebo), this value was reduced by only 6 mm.
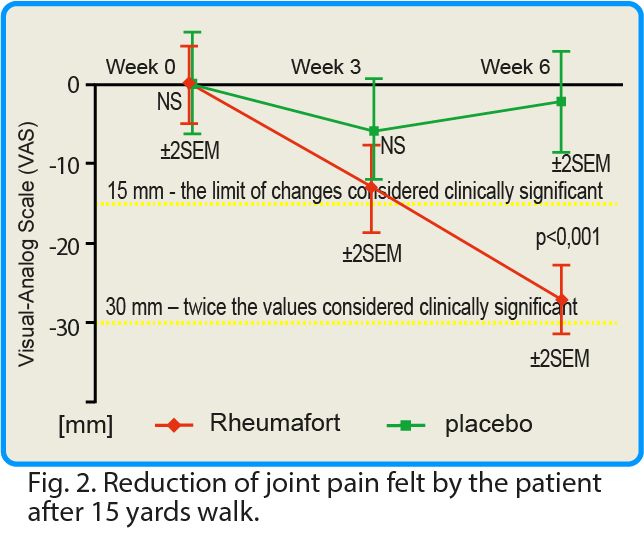
click this graph to magnify it
In many clinical studies, it was assumed that a change in the value of pain intensity (assessed using the VAS scale) if it is below 15 mm, is of little clinical significance1. We have assessed pain intensity change (VAS scale) at 30 mm – a doubled limit considered as significant (2x 15 = 30 mm).
The WOMAC Index
The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) is widely used in the evaluation of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. WOMAC Index was developed in 1982 at Western Ontario and McMaster Universities. WOMAC is available in over 65 languages and has been linguistically validated.[2,3] It is a self-administered questionnaire consisting of 24 items divided into 3 subscales:[2]
- Pain (5 items): during walking, using stairs, in bed, sitting or lying, and standing upright
- Stiffness (2 items): after first waking and later in the day
- Physical Function (17 items): using stairs, rising from sitting, standing, bending, walking, getting in / out of a car, shopping, putting on / taking off socks, rising from bed, lying in bed, getting in / out of bath, sitting, getting on / off toilet, heavy domestic duties, light domestic duties
As assessed by the WOMAC Integrated Osteoarthritis Index, the Rheumafort group showed a highly statistically significant reduction in symptoms (pain, stiffness and joint function) (p≤ 0.001) compared to the placebo control group after 6 weeks. The results are presented graphically below.
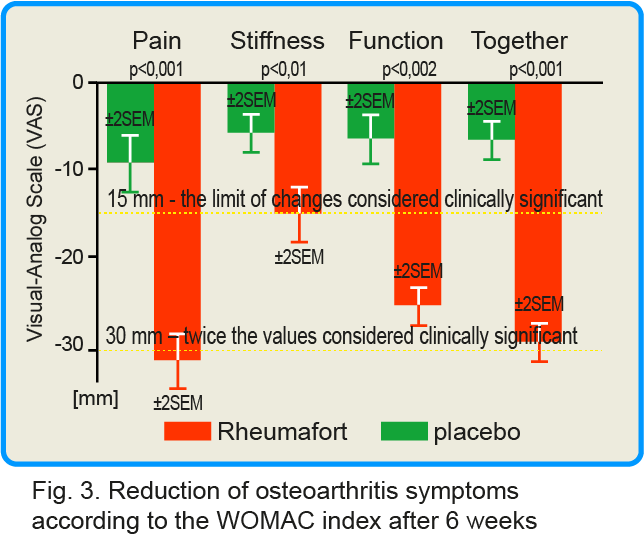
click this graph to magnify it
The group receiving the investigated preparation showed reduction of the three symptoms assessed together by 23 mm, while in the group receiving the placebo it was only 5 mm. In the group receiving the preparation containing plant extracts, the average reduction in pain intensity was 28 mm, the reduction in stiffness was 14 mm, and the reduction in joint function impairment was 22 mm. For comparison, in the placebo group, these parameters decreased by 9 mm, 4 mm and 5 mm, respectively.
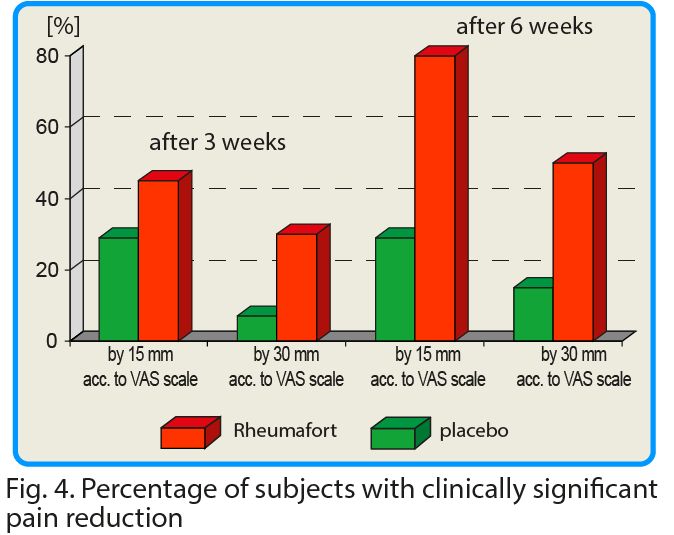
click this graph to magnify it
Conclusions
- The tested preparation containing plant extracts shows clinically significant, beneficial effects in osteoarthritis.
- Supplementing the daily diet with plant extracts by people suffering from osteoarthritis leads to the improvement of the function of the affected joint (determined by the WOMAC study) and the reduction of symptoms associated with the disease (pain and stiffness).
- Taking a preparation containing plant extracts by people with osteoarthritis leads to an improvement in their quality of life.
- During the 6-week observation, no significant side effects or side effects related to the intake of plant extracts were observed.
Cyclooxygenases and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
In recent years, it has been established that there are 3 isoenzymes COX-1, COX-2 and COX-3, which initiate the pathway of transformation of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins and related lipid mediators. COX-3 is an enzyme that is encoded by the PTGS1 (COX1) gene, but is not functional in humans. COX-3 is the third and most recently discovered cyclooxygenase (COX) isozyme, the others being COX-1 and COX-2. The COX-3 isozyme is encoded by the same gene as COX-1, with the difference that COX-3 retains an intron that is not retained in COX-1.[6,7]
COX-3 was actually discovered in 2002, and been found to be selectively inhibited by paracetamol, phenacetin, antipyrine, dipyrone, and some NSAIDs in rodent studies.[6,7] Acetaminophen is thought of as a mild analgesic and antipyretic suitable, at best, for mild to moderate pain. Its site of action has recently been identified as a COX-3 isoenzyme, a variant of the COX-1 enzyme[7]. This discovery raises the possibility of developing more potent and selective drugs targeting the site.
Cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1/PTGS1 – prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1) so-called constitutive is constantly present in most tissues and is responsible for the production of arachidonic acid of certain substances (eicosanoids) necessary to maintain systemic homeostasis. COX-1 is inhibited by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin. Thromboxane A2, the major product of COX-1 in platelets, induces platelet aggregation. The inhibition of COX-1 is sufficient to explain why low dose aspirin is effective at reducing cardiac events.
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2/PTGS2 – prostaglandin-endoperoxidase 2) so-called inducible is responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins[8] (PGD2, PGE2, PGF2α).
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are widely used in the treatment of pain syndromes, inflammation, diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, dysmenorrhea, toothache and headache. NSAIDs are also commonly used as antipyretics. All classical NSAIDs inhibit all 3 COX isoenzymes to varying degrees, so they can be considered non-selective. Due to the inhibition of COX-1, the use of these drugs is associated with an increased risk of ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa and serious complications of the upper gastrointestinal tract – bleeding, perforation or blockage. Moreover, they can cause complaints such as dyspepsia and abdominal pain. Therefore, high hopes were pinned on coxibs, i.e. selective COX-2 inhibitors, introduced in the late 1980s. Unfortunately, it soon turned out that the use of coxibs may contribute to the appearance of serious complications.
Comparison of investigated preparation with selective COX-2 inhibitor
The investigated preparation containing plant extracts was compared with the selective cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitor Celecoxib, which is an effective analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug. The comparison was made by overlaying the published results of celexib studies with the obtained results of our preparation. The chart below compares the analgesic effects of plant extracts and coxib. Both preparations were studied in the same way, except that those taking Celecoxib were evaluated after 2 and 6 weeks, and the investigated preparation after 3 and 6 weeks. It turned out that taking a preparation with plant extracts gives patients with osteoarthritis a similar analgesic effect as celecoxib.
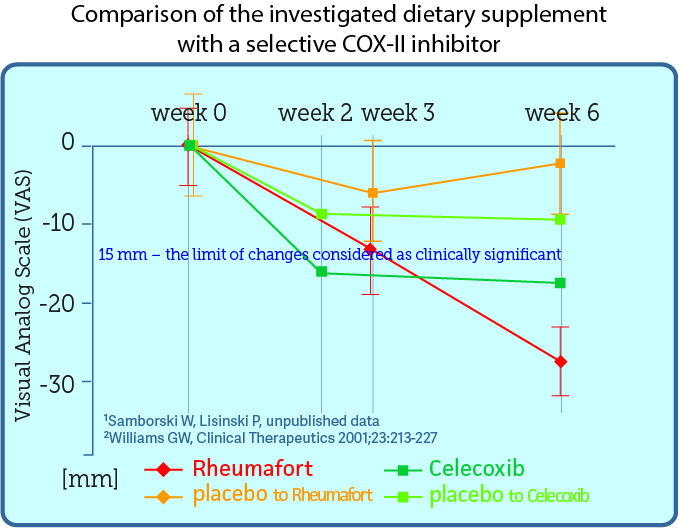
click the graph to magify
Based on data from the article Comparison of Once-Daily and Twice-Daily Administration of Celecoxib for the Treatment of Osteoarhritis of the Knee. published in 2001 in the Journal Clinical Therapeutics. You can read the publication (in English) on the previous tab in the paragraph.
References
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. J Pain 2008;9:105-21.
- American College of Rheumatology. Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). http://www.rheumatology.org/practice/clinical/clinicianresearchers/outcomes-instrumentation/WOMAC.asp. (accessed 12 July 2013).
- WOMAC Osteoarthritis Index. http://www.womac.org/womac/index.htm. (accessed 12 July 2013).
- Theiler R, Spielberger J, Bischoff H.A., Bellamy N, Huber J, Kroesen S. Clinical evaluation of the WOMAC 3.0 OA Index in numeric rating scale format using a computerized touch screen version [abstract]. OSTEOARTHR CARTILAGE 2002;10(6):479-481
- Bellamy N, Wilson C, Hendrikz J, Whitehouse S.L., Patel B, Dennison S, Davis T. Osteoarthritis Index delivered by mobile phone (m-WOMAC) is valid, reliable, and responsive [abstract]. J CLIN EPIDEMIOL 2011;64(2):182-190
- Botting R (June 2003). COX-1 and COX-3 inhibitors Thromb. Res. 110 (5–6): 269–72.
- Chandrasekharan NV, Dai H, Roos KL, Evanson NK, Tomsik J, Elton TS, Simmons DL (October 2002). COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (21): 13926–31.
- Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA. Prostaglandins and inflammation Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 May; 31(5): 986–1000.
- US Food and Drug Administration: COX-2 Selective (includes Bextra, Celebrex, and Vioxx) and Non-Selective Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) 2005.
2 Chondrocytes - are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycanscell producing joint cartilage. Chondrocytes do not have blood vessels they receive nourishment from synovial liquid exclusively.
3Radiological Assessment of Osteoarthritis described by Kellgren-Lawrence evaluation of OA progression acc to radiological criteria. Stage II - small progression of changes: visible osteophytes, no change or discreet narrowing of the joint space; stage III - moderate escalation of changes: moderate osteophytes, visible narrowing of the joint space, possible joint deformation.
4 Double blind study - a medical study in which both the subjects participating and the researchers are unaware of when the experimental medication or procedure has been given. Double-blinded studies are often used when initial studies shows particular promise.
5 Randomisation – random classification of subjects into comparative groups in order to eliminate the influence of uncontrolled variables on the study results.
6 Wash-out period – is the pre-determined period of time in a clinical trial receive no active medication so that all traces of the drug are washed out of a patient’s system. This typically happens between treatment periods.
7 Placebo - it is a product / procedure that looks identical to the investigated one but does not provide active ingredients / therapeutic action. In medical research, placebo is applied as control and depends on the use of measured suggestion. Sometimes patients given a placebo treatment will perceive an improvement - a phenomenon commonly called the placebo effect. Properly made study that evaluates subjective symptoms like e.g. pain always shows betterment after placebo administration - so called placebo effect. Missing placebo effects suggests methodological error.
8 Likerta scale – is a psychometric scale commonly involved in research. This is five-level scale where a tested person choose this value, which corresponds with his feeling best.
9 Questionnaire SF-12 is a selected part of questionnaire SF-36 for assessement of general health and quality of life related to physical activity.
10 WOMAC Index - Western Ontario and McMaster Osteoarthritis Index, also named WOMAC scale na integrated is a widely used, proprietary set of standardized questionnaires used by health professionals to evaluate the condition of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee and hip, including pain, stiffness, and physical functioning of the joints.
11 Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is a psychometric response scale which can be used in questionnaires. It is a measurement instrument for subjective characteristics or attitudes that cannot be directly measured. When responding to a VAS item, respondents specify their level of agreement to a statement by indicating a position along a continuous line between two end-points.